
Geography
-
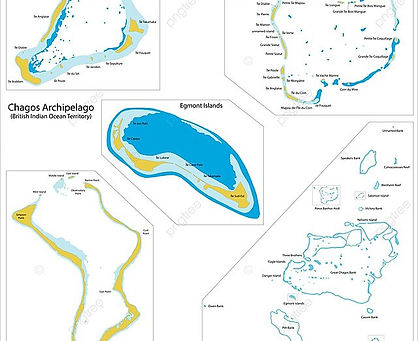
Chagos Archipelago: a remote, coral‐atoll–rich territory spread across tens of thousands of km² with a tiny land footprint.
-
Peros Banhōs: significant for its size, historic human settlement, and protected status.
-
Salomon Atoll: smaller, was less inhabited, valued today for conservation and limited tourism.
-
These features are emblematic of the archipelago's flat, reef-based geography and ecological richness.

Chagos Archipelago
-
Consists of seven coral atolls plus around 60 islands in the central Indian Ocean, approximately 500 km south of the Maldives
-
Total land area is roughly 56 km², scattered across a vast oceanic area exceeding 50,000 km², mostly made up of submerged coral banks
-
Situated between coordinates 4°54'–7°39'S latitude and 70°14'–72°37'E longitude, the atolls rest atop the Chagos–Laccadive submarine Ridge
-
Islands are low-lying and flat (under 2 m above sea level), with Diego Garcia as the highest point at around 15 m elevation
-
The archipelago forms one of the world's largest no-take marine protected areas, established in 2010

Regional Context & Topography
-
Positioned ~500 km south of the Maldives, 1,680 km NE of Rodrigues (Mauritius), and also relatively remote from Seychelles and Cocos Islands
-
Geologically underpinned by a submerged volcanic ridge tied to the Réunion hotspot, creating a pattern of coral atolls with no consistent linear arrangement.
-
Contains the Great Chagos Bank—the world’s largest coral atoll—along with Peros Banhōs and Salomon, and southern atolls Egmont and Diego Garcia.

Peros Banhōs Atoll
-
A medium-sized coralline atoll with a total area of approximately 503 km², but only about 9.6 km² of land spread over some 32 islets.
-
Features a roughly 20 km diameter lagoon, ringed by a continuous reef with flat, sandy islets often crowned by coconut palms.
-
The largest island is Île du Coin, formerly supporting plantations and a jetty; other notable islets include Île Manoël, Île Pierre, and Île Diamant.
-
Part of the atoll is designated as a Strict Nature Reserve (east of a line between Moresby and Fouquet Islands) and is a designated Important Bird Area, hosting ~14,000 pairs of sooty terns in 2004.
-
It has a documented history of habitation until the population was expelled in the 1970s .

Salomon Islands (Salomon Atoll)
-
A smaller atoll, spanning around 3.6 km² of land across 11 islets and enclosing a coral lagoon.
-
Lies just east of Peros Banhōs within the northern part of Chagos.
-
Mostly uninhabited, it was formerly used for coconut plantations.

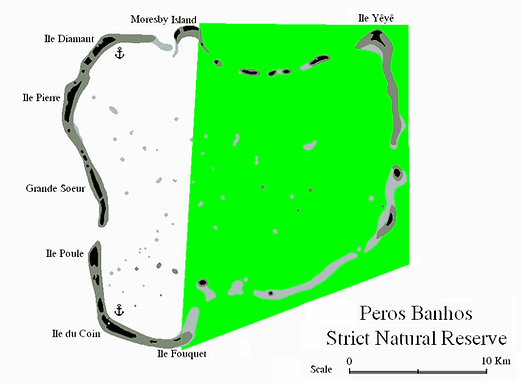

Courtesy: hr.wikipedia.org/wiki/peros-banhos & academia-lab.com/enciclopedia/peros-banhos)